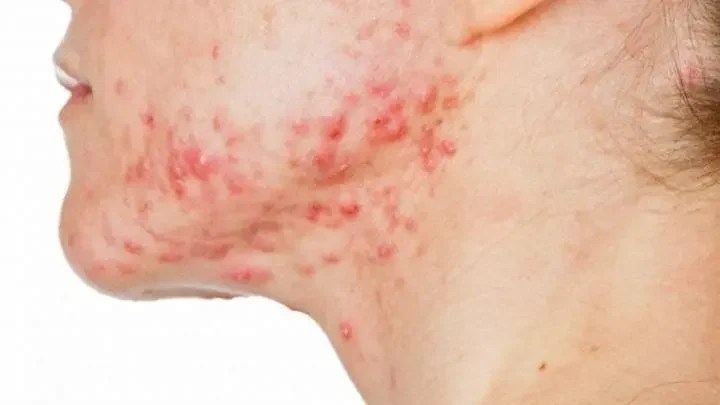
If you are reading this blog, there is a high chance that you already think you have Atopic dermatitis or as we say in layman’s term, eczema. I have personally battled or should I say still battling severe atopic dermatitis. Over time, I’ve received numerous questions about how to determine if you have this condition, so I’m here to guide you through the process.
Recognizing the Signs and Symptoms
The first step in identifying atopic dermatitis is understanding its symptoms. Ask yourself the following questions:
- Do you frequently experience itchy, inflamed skin?
- Do you get recurring acne that refuses to clear up?
- Do you suffer from sudden hot flashes on your skin?
- Do you notice scaly, irritated patches on your arms and legs?
- Do you have broken skin barrier?
- Do you often have respiratory symptoms like sneezing, nasal congestion, or breathing difficulties?
If you answered “yes” to most of these, it’s time to consider getting tested for allergies, as these symptoms are commonly associated with atopic dermatitis.
Essential Tests for Diagnosis
To confirm whether you have atopic dermatitis, you should undergo the following medical tests:
- IgE Test– An IgE (Immunoglobulin E) test measures the levels of IgE antibodies in your blood. These antibodies play a crucial role in your body’s allergic response. Elevated IgE levels indicate that your immune system is overreacting to allergens, which can be anything like pollen, dust, pet dander, or any food items. High IgE levels suggest that you may have allergies to specific substances. In some cases, elevated IgE may indicate a parasitic infection. In some very rare cases, abnormal IgE levels can also indicate immune system dysfunction. So basically, this is the first step to check whether or not you have allergies. If your IgE test results are high, it is recommended to do allergy-specific tests (like a skin prick test or Phadia Top test) to identify specific allergens that are triggering the symptoms.
- Phadia Top Test: Phadia Top test is a comprehensive allergy screening test that helps identify allergic sensitivities to multiple allergens at once. It is a type of specific IgE blood test that detects the presence of IgE antibodies against common allergens like-
- Food Allergies – It screens for common food allergens such as milk, eggs, peanuts, seafood, wheat, and soy.
- Environmental Allergies – It identifies reactions to pollen, dust mites, pet dander, mold, and other airborne allergens.
- Inhalant Allergies – Helps diagnose allergic responses to substances like grass, trees, and weeds.
- Cross-Reactive Allergens – The test can detect patterns of cross-reactivity (e.g., people allergic to birch pollen may also react to certain fruits).
- Skin Prick Test: A skin prick test (SPT) is a diagnostic test used to identify specific allergens that may be triggering allergic reactions in a person. It is a quick and minimally invasive procedure commonly used to diagnose environmental, food, and contact allergies. Unlike blood tests like IgE or Phadia Top, which measure antibody levels, a skin prick test directly observes how your skin reacts to allergens in real-time, making it one of the most effective allergy tests available. How the Test Works:
- Small drops of suspected allergens are placed on the skin (usually the forearm or back).
- The skin is lightly pricked with a tiny needle to allow allergens to enter the surface.
- If you’re allergic, a small red, itchy bump (wheal) will appear within 15-20 minutes at the test site.
Finding the Right Treatment
While self-awareness and learning from others’ experiences can be incredibly helpful, consulting a specialized allergist and a dermatologist is crucial for personalized treatment and for long-term health (both skin health and overall health).
I’m sharing my honest journey with atopic dermatitis—what has worked for me, what hasn’t, and how I’m healing my skin. If you’re looking for guidance and want to achieve healthier skin, stay tuned in this space. Let’s navigate this journey together.



Leave a comment